GM Builders!
The GG22 Allo Builders Advancement Round has concluded, and we’re excited to share the outcomes, insights, and lessons learned. This round not only distributed funding to outstanding projects but also furthered our mission to enhance grant infrastructure and enable equitable resource allocation in the Allo ecosystem.
Round Overview
Key Metrics
- Total Donations: $5,273.06
- Matching Funds Available: $25,000 USDGLO
- Unique Contributors: 333
- Number of Contributions: 934
- Participating Projects: 17
- Average Contribution: $15.84
Passport Usage
- 100% of contributor addresses were scored using the Passport Model-Based Detection System.
- 110 Users (33.0%) received full matching (passport model score over 50).
- 21 Users (6.3%) received partial matching (passport model score between 25 and 50).
- Full Matching: Contributions matched at 100% of the calculated amount.
- Partial Matching: Contributions matched between 50-100% based on the score.
This system effectively incentivized legitimate users to strengthen their digital identities, ensuring fairer distribution while protecting matching funds from Sybil attacks and airdrop farmers.
Explore the full results in detail:
https://qf-calculator.fly.dev/?round_id=636&chain_id=42161
COCM: Improving Fairness in Matching
COCM vs. QF
The adoption of COCM over traditional Quadratic Funding (QF) highlighted the value of filtering connections and weighting contributions based on relationships, leading to more equitable outcomes for ecosystem grant programs.
Balancing between mechanisms (e.g., COCM and QF) can provide flexibility for future rounds depending on goals.
Key Takeaways from COCM Results
1. Balancing Over-Concentrated Networks: Amplifying contributions from high-context donors and mitigating bot-like behavior on grants for, the COCM model mitigated the influence of isolated wallets and ensured fair matching allocations.
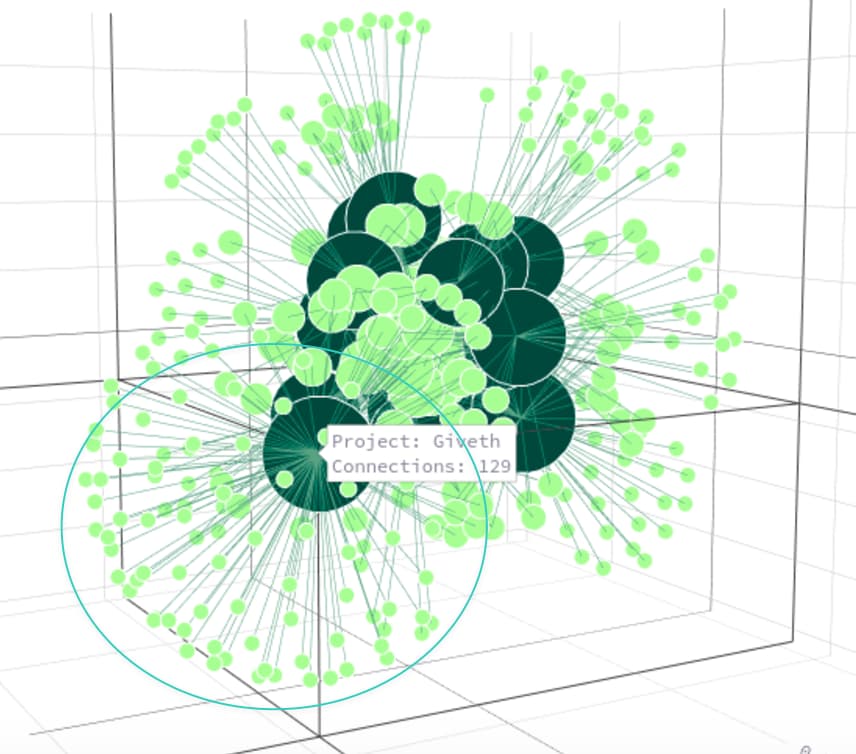
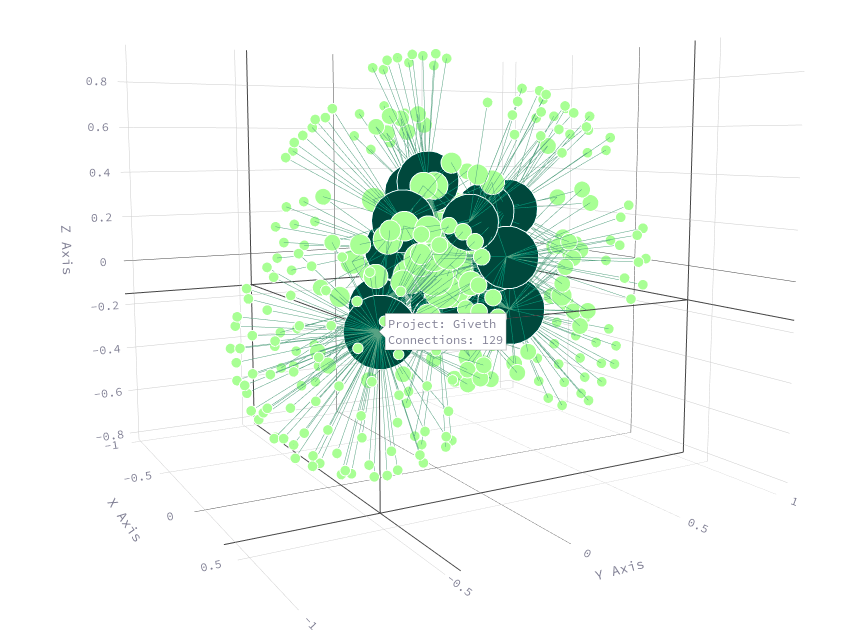
2. Projects like Giveth and VoiceDeck saw reduced matching under COCM compared to QF due to contributions coming from wallets that donated to just one project. This reduction highlights COCM’s ability to discourage over-concentrated support and encourage a more diverse backing.
3. Projects such as Open Source Observer, 1Hive Gardens, and Karma GAP received significant boosts in matching through COCM due to their support coming from wallets with a diversity of connections.
Matching Models Breakdown
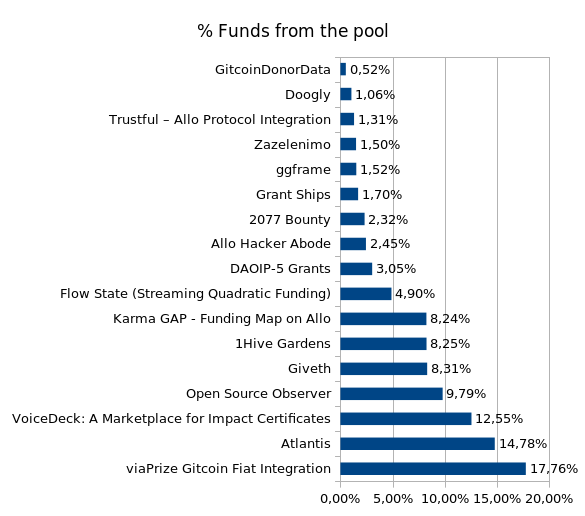
The COCM model was used to calculate matching funds. Below are the top 10 projects based on COCM results:
| Project Name | Matching Amount (COCM) | Matching Amount (QF) | Δ Match |
|---|---|---|---|
| viaPrize Gitcoin Fiat Integration | $4,438.77 | $3,500.45 | $938.32 |
| Atlantis | $3,694.93 | $3,373.39 | $321.54 |
| VoiceDeck: A Marketplace for Impact Certificates | $3,138.43 | $5,000.00 | -$1,861.57 |
| Open Source Observer | $2,447.41 | $871.77 | $1,575.64 |
| Giveth | $2,077.76 | $4,109.78 | -$2,032.02 |
| 1Hive Gardens | $2,061.28 | $946.32 | $1,114.96 |
| Karma GAP - Funding Map on Allo | $2,059.52 | $993.49 | $1,066.03 |
| Flow State (Streaming Quadratic Funding) | $1,223.86 | $758.18 | $465.68 |
| DAOIP-5 Grants Standard by DAOstar - Improving the web3 grants ecosystem for everyone | $761.56 | $341.96 | $419.60 |
| Allo Hacker Abode | $612.28 | $1,722.62 | -$1,110.34 |
These results reflect how matching was distributed, with the COCM model ensuring contributions from high-context donors were prioritized while managing coordination effects.
This approach resulted in a more equitable distribution of funds, aligned with the ethos of decentralized public goods funding.
Key Round Insights
1. Enhanced Sybil Resistance
- Gitcoin Passport Integration:
- 100% of contributor addresses were verified using Gitcoin Passport, ensuring credibility and reducing fraudulent activity.
2. Improving Matching Mechanism
-
COCM vs. Quadratic Funding:
- COCM outperformed traditional QF by focusing on meaningful relationships between wallets, aligning resources with high-context donors who provided stronger signaling.
- further prioritized wallets backed by diversified connections, amplifying contributions impact and mitigating bot-like behavior.
- COCM outperformed traditional QF by focusing on meaningful relationships between wallets, aligning resources with high-context donors who provided stronger signaling.
-
Matching Cap:
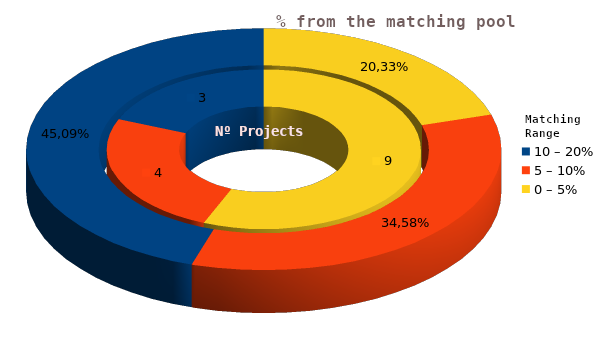
We could have achieved even greater equity within the round with a Matching Cap set at 18% instead of 20%. Since none of the projects reached this value, and only 3 projects received over 10% of the funds, while 4 projects secured between 5% and 10%, and 9 projects received between 0% and 5%.
3. Community Engagement
- The round attracted a diverse set of projects and contributors, emphasizing the ecosystem’s growing vibrancy.
- 17 Participating Projects: Spanning a range of impact areas, from fiat integrations to reputation systems and impact tracking tools.
User Experience Enhancements
The updated Grantstack Dashboard simplified round management and transparency:
- Provided clear visualizations of wallet connections, donor behaviors, and matching allocations.
- Enabled quick comparisons between COCM and QF models for informed decision-making.
- Streamlined payout processes with integrated features like member addition and fund distribution.
Lessons Learned
1. Matching Mechanisms Matter
- COCM proved effective for this grant type, but balancing between mechanisms (e.g., COCM and QF) can provide flexibility for future rounds depending on goals.
2. Transparency is Key
- The dashboard visualizations and Passport integration demonstrated the importance of clear, accessible data in fostering trust and fairness.
3. Future Opportunities
- Continue scaling the matching cap to maintain balance across larger matching pools.
- Explore ways to onboard more diverse contributors and projects into the ecosystem.
Next Steps
1. Grant Tracking
- Track how the matching funds are creating impact, using milestones on https://gap.karmahq.xyz
2. Expand Engagement
- We aim to enhance education and outreach to onboard more projects and contributors for future rounds.
3. Build on Success
- Use insights from this round to refine matching mechanisms and grow the Allo ecosystem with innovative, impactful projects.
Thank You, Builders!
A massive thank you to everyone who participated, contributed, or supported this round. Together, we are shaping the future of decentralized funding and public goods. Your work inspires us to keep pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
For questions, feedback, or ideas for future rounds, feel free to reach out. Let’s keep building!
Stay awesome,
The Allo Builders Team